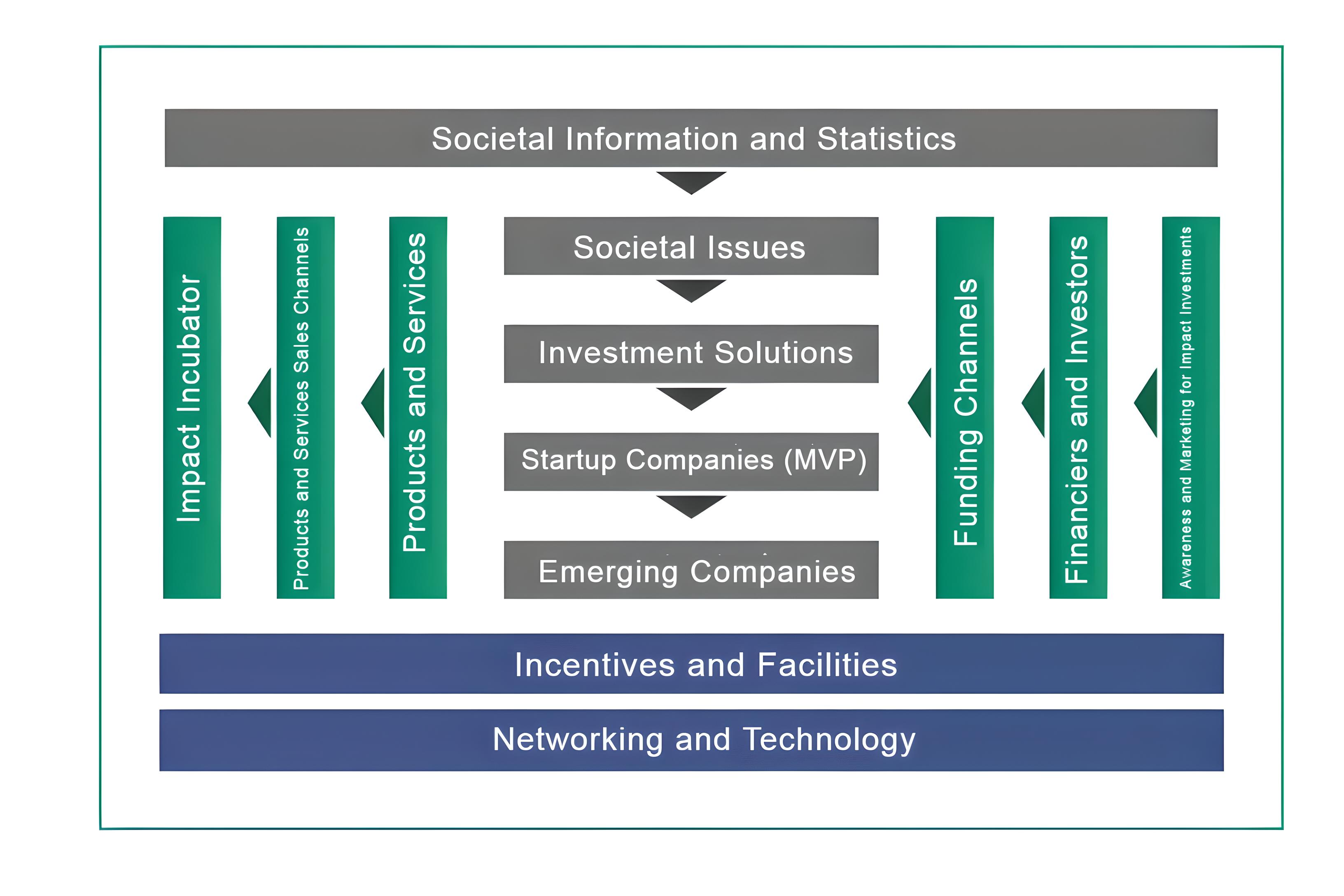
The availability of accurate and comprehensive data contributes to rational and effective decision-making, as well as to the identification of priority social and environmental challenges, both locally and globally. In particular, data is the first step in the influential enterprise industry, mainly linked to governance, impact measurement and knowledge ecosystems. This component also provides data on society, government and the business community, also data on economic, demographic, social and environmental fields. It also aims to achieve authentic, comprehensive, up-to-date and accessible data for all stakeholders.
Societal issues are those that affect different groups in society or the environment, and that can be addressed by impactful projects. Societal issues are the component that deals with data, information and analyses it, with the aim to presenting phenomena, societal problems and the underlying causes of such problems in society, as well as studying their relevance to other problems and phenomena. This component is mainly linked to data being the source on which it is based, as society’s issues are direct inputs to the investment solutions component.
Investment solutions are specifically designed to address the challenges and underlying issues faced by society. It is essential that business models are innovatively crafted to contribute to solving societal problems while meeting profitability targets. These solutions encompass strategies and tools in the field of impact investment, aimed at maximizing returns and managing associated risks in a professional manner. Crucially, the business model prioritizes social or environmental objectives, ensuring alignment between social and financial returns. In this context, business indicators also incorporate social or environmental metrics
Companies are entities that provide services and products to address issues, either through their business models or through the services and products they offer. Examples of such organizations include social entrepreneurship companies, cooperatives, associations, and other forms. This component supports the transitional phase of emerging organizations that are new and developing a distinctive product or service for launch in the market. As organizations mature, they achieve sustainability and preparedness for business expansion and community service.
This component is an essential part of enabling organizations’ access to the market and providing various supportive services that maximize impact and profitability. This is accomplished through the use of marketing and awareness techniques to promote and disseminate the concept of impactful investment, thereby increasing demand for products and services. Its primary objective is to achieve attractive financial returns while also enhancing consumer demand for these services and products
It is the means or channel that facilitates, manages, and monitors the flow of funds between financiers, whether individuals or organizations, as well as between funding or investment opportunities, whether for studying societal issues, producing investment solutions, or supporting mature and emerging companies. This component is interconnected with financiers, investors, and the accelerator of the influential enterprise industry, as well as with the outcomes of impact, where it contributes to the returns
Any individual or entity committed to the establishment of capital with the anticipation of receiving financial and social returns within specific conditions and specifications to accomplish a social objective, whether it be studying societal issues, developing investment solutions, or supporting mature and emerging companies. Investors may originate from the private, public, or non-profit sector, and funding forms encompass grants, loans, investments, and all other funding avenues.
The environment includes all capabilities, incentives, and legislation related to the investment sector, which are directly or indirectly impacted. This component essentially provides the necessary frameworks, enabling parties to operate within the ecosystem and share value. The environmental component includes regulations, legislation, grants, labor subsidies, tax or rent exemptions, as well as the removal of certain controls and improvements in infrastructure. In general, government entities play an important role in empowering the impactful investment market through this component.
Capacity-building and knowledge are the key pillars that enhance the characteristics, efficiency, productivity, and performance of individuals and organizations. This component aims to develop the skills, capacities, actions, and resources necessary for individuals and organizations to efficiently fulfill their roles in the ecosystem, as well as to adapt to and address variables and risks. Additionally, this component works to provide knowledge capabilities and services for the development of the sector and the ecosystem. It is also closely linked with the cycle of returns, impact, and financing, providing the ecosystem leader with forward-looking visions to aid in market development.
The Ecosystem Leader is the party responsible for the leadership, structure, and performance management of the ecosystem. Ecosystems, in general, are built upon common goals and values, necessitating coordination to efficiently and effectively achieve them. It should be noted that the leader of the ecosystem does not operate hierarchically, but rather systematically, collaborating with various partners to enhance the ecosystem’s shared value. One of the roles of the ecosystem leader is to engage in advocacy in market policymaking and utilize their influence to engage with government departments, service providers, investors, and broader stakeholders to address risks, constraints, and challenges. Additionally, the roles of the ecosystem leader include setting governance frameworks, managing risks at the ecosystem level, and establishing the necessary measurement frameworks to ensure the sustainability of the ecosystem through learning, innovation, accountability, indicators, and impact.

We are an investment holding company committed to fostering and advancing the impact investment ecosystem. We focus on a strategic roadmap for effective investment, enhancing the existing ecosystem, and expanding the scope of investment opportunities.
Copyright by Invest In Impact © 2024. All rights reserved. Powered by SSASOFT
Invest In Impact
We firmly believe that the internet should be available and accessible to anyone, and are committed to providing a website that is accessible to the widest possible audience, regardless of circumstance and ability.
To fulfill this, we aim to adhere as strictly as possible to the World Wide Web Consortium’s (W3C) Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.1 (WCAG 2.1) at the AA level. These guidelines explain how to make web content accessible to people with a wide array of disabilities. Complying with those guidelines helps us ensure that the website is accessible to all people: blind people, people with motor impairments, visual impairment, cognitive disabilities, and more.
This website utilizes various technologies that are meant to make it as accessible as possible at all times. We utilize an accessibility interface that allows persons with specific disabilities to adjust the website’s UI (user interface) and design it to their personal needs.
Additionally, the website utilizes an AI-based application that runs in the background and optimizes its accessibility level constantly. This application remediates the website’s HTML, adapts Its functionality and behavior for screen-readers used by the blind users, and for keyboard functions used by individuals with motor impairments.
If you’ve found a malfunction or have ideas for improvement, we’ll be happy to hear from you. You can reach out to the website’s operators by using the following email
Our website implements the ARIA attributes (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) technique, alongside various different behavioral changes, to ensure blind users visiting with screen-readers are able to read, comprehend, and enjoy the website’s functions. As soon as a user with a screen-reader enters your site, they immediately receive a prompt to enter the Screen-Reader Profile so they can browse and operate your site effectively. Here’s how our website covers some of the most important screen-reader requirements, alongside console screenshots of code examples:
Screen-reader optimization: we run a background process that learns the website’s components from top to bottom, to ensure ongoing compliance even when updating the website. In this process, we provide screen-readers with meaningful data using the ARIA set of attributes. For example, we provide accurate form labels; descriptions for actionable icons (social media icons, search icons, cart icons, etc.); validation guidance for form inputs; element roles such as buttons, menus, modal dialogues (popups), and others. Additionally, the background process scans all the website’s images and provides an accurate and meaningful image-object-recognition-based description as an ALT (alternate text) tag for images that are not described. It will also extract texts that are embedded within the image, using an OCR (optical character recognition) technology. To turn on screen-reader adjustments at any time, users need only to press the Alt+1 keyboard combination. Screen-reader users also get automatic announcements to turn the Screen-reader mode on as soon as they enter the website.
These adjustments are compatible with all popular screen readers, including JAWS and NVDA.
Keyboard navigation optimization: The background process also adjusts the website’s HTML, and adds various behaviors using JavaScript code to make the website operable by the keyboard. This includes the ability to navigate the website using the Tab and Shift+Tab keys, operate dropdowns with the arrow keys, close them with Esc, trigger buttons and links using the Enter key, navigate between radio and checkbox elements using the arrow keys, and fill them in with the Spacebar or Enter key.Additionally, keyboard users will find quick-navigation and content-skip menus, available at any time by clicking Alt+1, or as the first elements of the site while navigating with the keyboard. The background process also handles triggered popups by moving the keyboard focus towards them as soon as they appear, and not allow the focus drift outside it.
Users can also use shortcuts such as “M” (menus), “H” (headings), “F” (forms), “B” (buttons), and “G” (graphics) to jump to specific elements.
We aim to support the widest array of browsers and assistive technologies as possible, so our users can choose the best fitting tools for them, with as few limitations as possible. Therefore, we have worked very hard to be able to support all major systems that comprise over 95% of the user market share including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, Opera and Microsoft Edge, JAWS and NVDA (screen readers).
Despite our very best efforts to allow anybody to adjust the website to their needs. There may still be pages or sections that are not fully accessible, are in the process of becoming accessible, or are lacking an adequate technological solution to make them accessible. Still, we are continually improving our accessibility, adding, updating and improving its options and features, and developing and adopting new technologies. All this is meant to reach the optimal level of accessibility, following technological advancements. For any assistance, please reach out to